Measuring Metallic Corrosion with Half Cell Potential Test
When reinforcing
steel corrodes inside concrete, an electro-chemical process occurs and its
characteristics can be identified with a half-cell potential (HCP) measurement,
also known as a ‘half cell potential test’. HCP measures metallic corrosion to
determine the regions of potential corrosion and the risk it can impose on the
structure. Date interpretation is nuanced and specific to particular sites, but
generally a more negative potential means a risk of corrosion occurring in
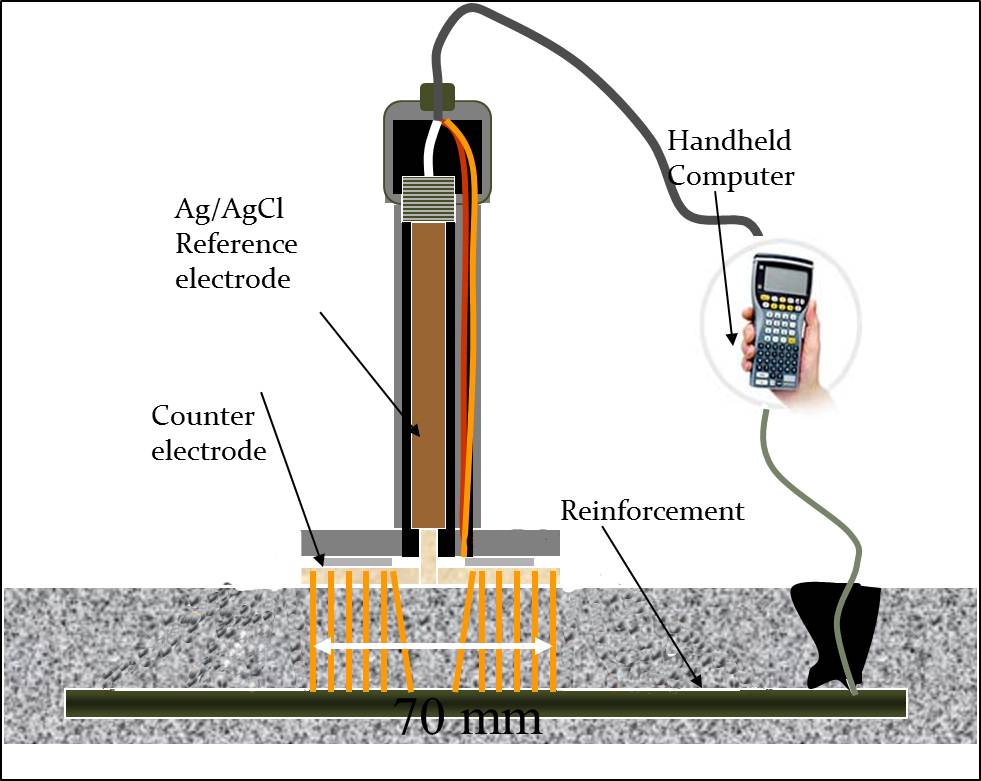
unsaturated marine exposed concrete. To conduct the test, an electrode is used
to form one part of the bimetal cell, while the reinforcing steel within the
concrete serves as the other half. Silver/silver chloride in a potassium
chloride solution or a simple Copper/Copper Sulphate cell is the ideal
reference electrode for use on-site. An electrode that is made of copper/copper
sulphate is widely used, too.
An advanced half cell
potential meter is a great instrument to have for a more reliable way to locate
corrosion in embedded reinforcing steel. The best meters are versatile and can
work with either a silver/silver chloride or copper/copper sulphate half-cell.
Cover concrete is
locally removed over an appropriate bar, and the electrical connection is
established to the steel. During the test, you need to ensure electrically
continuous steel by determining the resistance between the two points which are
widely separated. The reinforcing bar is linked to a half-cell through a
meter’s internal digital voltmeter and readings of the half-cell potential are
identified about regular grid points to create a prospective map of the area.
Advanced machines may offer a wheel electrode for quick data collection.
Operators may plot
contour lines between the points of equal potential while measuring
metallic corrosion with a half cell potential meter. That way they can
indicate that those areas possess the highest risk of corrosion. It is
recommended that you expose and inspect reinforcing steel in places where low
and high risks of corrosion exist as a final point of data to confirm an
inspection method. That way, you can estimate the rate of corrosion and
evaluate the need for repair or further investigation.
Comments
Post a Comment